Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) is a holistic approach combining manual techniques with exercise and education. It addresses the whole body, focusing on restoring function and well-being.
1.1 Definition and Overview
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) is a holistic, evidence-based approach that combines manual techniques with therapeutic exercises and patient education. It focuses on addressing the whole body, emphasizing the interconnectedness of physical, emotional, and functional systems. IMT aims to restore optimal movement, reduce pain, and enhance overall well-being by identifying and treating underlying dysfunctions. This method integrates various manual therapies, such as soft tissue mobilization and joint manipulation, with targeted exercises to promote long-term recovery and health. It is practiced by licensed professionals, including physical therapists, osteopaths, and chiropractors, who tailor treatments to individual needs, ensuring a patient-centered and outcome-driven approach.
1.2 Historical Development
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) has its roots in ancient healing practices, such as Ayurveda and traditional Chinese medicine, which emphasized manual techniques for restoring balance. In the 19th century, modern manual therapies like osteopathy and chiropractic medicine emerged, laying the groundwork for IMT. The 20th century saw the integration of these practices with physical therapy and exercise science, leading to a more holistic approach. Over time, IMT evolved to incorporate evidence-based methodologies and advanced techniques, blending soft tissue mobilization, joint manipulation, and therapeutic exercises. Today, it is recognized as a comprehensive, patient-centered modality, continually refined by scientific research and clinical outcomes.
1.3 Key Principles and Philosophy
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) is rooted in the principle of treating the whole person, addressing physical, emotional, and functional aspects. It emphasizes a holistic, evidence-based approach, blending manual techniques with therapeutic exercises. IMT focuses on restoring optimal function by identifying and addressing dysfunction at the cellular and systemic levels. The philosophy centers on patient-centered care, ensuring treatments are tailored to individual needs. It promotes empowerment through education and movement, fostering long-term well-being. By integrating diverse therapeutic modalities, IMT aims to enhance the body’s natural healing processes, ultimately restoring balance and improving quality of life. This approach is both preventive and restorative, targeting the root cause of dysfunction rather than just symptoms.
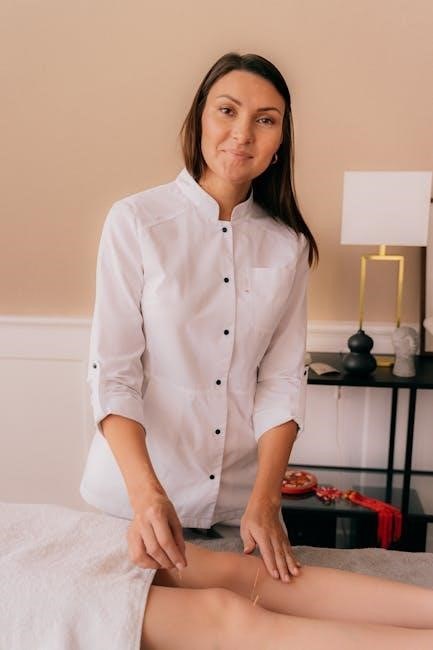

Core Concepts and Techniques
Integrated Manual Therapy combines manual examination, soft tissue mobilization, joint mobilization, and therapeutic exercises to restore function and promote healing through a comprehensive, hands-on approach.
2.1 Manual Examination and Assessment
Manual examination and assessment are critical in Integrated Manual Therapy, involving hands-on evaluations to identify dysfunction in soft tissues, joints, and movement patterns. Techniques include palpation, range-of-motion testing, and strength assessments to pinpoint imbalances. These assessments guide the creation of personalized treatment plans, ensuring targeted interventions. By understanding the body’s structural and functional interconnections, therapists can address the root causes of pain and limitation, promoting effective and lasting outcomes for patients.
2.2 Soft Tissue Mobilization
Soft tissue mobilization is a cornerstone of Integrated Manual Therapy, focusing on techniques to improve mobility and function in muscles, tendons, and connective tissues. These methods address restrictions, scar tissue, and inflammation, enhancing blood flow and reducing pain. Therapists use hands-on approaches like massage, trigger point therapy, and myofascial release to restore tissue health. This treatment is tailored to individual needs, promoting recovery and preventing future issues. By targeting soft tissues, it complements joint and exercise therapies, ensuring a comprehensive approach to patient care and overall well-being. Soft tissue mobilization is essential for addressing chronic pain, sports injuries, and postural imbalances, making it a vital component of IMT practice.
2.3 Joint Mobilization and Manipulation
Joint mobilization and manipulation are techniques used to restore joint mobility, reduce stiffness, and improve range of motion. These methods involve targeted movements applied to specific joints, enhancing synovial fluid circulation and breaking down adhesions. Gentle oscillations or high-velocity thrusts are commonly employed, tailored to the patient’s condition. Joint mobilization is particularly effective for conditions like arthritis, chronic pain, and post-traumatic injuries. Manipulation often provides immediate relief from joint restrictions, promoting functional recovery. These techniques are integral to Integrated Manual Therapy, addressing joint dysfunction while complementing soft tissue and exercise-based approaches. Regular joint mobilization can prevent further degeneration and enhance overall joint health, making it a cornerstone of therapeutic practice.
2.4 Integration with Exercise and Movement
Exercise and movement are integral to Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT), enhancing the effects of manual techniques. Therapists design tailored exercise programs to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and restore functional movement patterns. These exercises often include stretching, resistance training, and proprioceptive drills. Movement education helps patients adopt proper posture and biomechanics, preventing further injury. By combining manual therapy with active exercises, patients achieve faster recovery and improved long-term outcomes. This integrated approach ensures that the body heals holistically, addressing both local and systemic issues. Regular movement practice also empowers patients to manage their conditions independently, fostering self-reliance and overall well-being.
Benefits and Applications
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) effectively addresses chronic pain, sports injuries, and neurological conditions. It enhances mobility, reduces inflammation, and promotes overall well-being through holistic, patient-centered care.
3.1 Chronic Pain Management
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) is highly effective in managing chronic pain by addressing the root causes of dysfunction. It combines soft tissue mobilization, joint manipulation, and targeted exercises to restore mobility and reduce inflammation. IMT emphasizes a holistic approach, considering the interconnection of the body’s systems. This method not only alleviates pain but also enhances overall well-being by improving nerve function and muscle relaxation. Patients often experience long-term relief as IMT empowers them to take an active role in their recovery through personalized exercises and lifestyle adjustments. By focusing on the whole body, IMT provides a comprehensive solution for chronic pain management, offering sustainable results and improved quality of life.
3.2 Sports Injury Rehabilitation
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) plays a crucial role in sports injury rehabilitation by promoting rapid recovery and restoring optimal function. It combines manual techniques, such as soft tissue mobilization and joint manipulation, with targeted exercises to address muscle imbalances and improve mobility. IMT helps athletes recover from injuries like strains, sprains, and tendonitis by reducing inflammation and enhancing blood flow to damaged tissues; The holistic approach of IMT ensures that the entire body is treated, not just the injured area, which often leads to better performance and reduced risk of future injuries. This method is particularly effective for athletes seeking to return to their sport with improved strength and flexibility, ensuring a seamless transition back to competition.
3.3 Neurological and Orthopedic Conditions
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) is highly effective in managing neurological and orthopedic conditions by addressing the interconnected systems of the body. For neurological conditions like stroke, spinal cord injuries, or Parkinson’s disease, IMT improves mobility, reduces muscle spasticity, and enhances motor control. Orthopedic conditions, such as arthritis, hip replacements, or fractures, benefit from IMT’s focus on joint stability, alignment, and soft tissue repair. Techniques like manual mobilization and targeted exercises help restore function, reduce pain, and prevent further degeneration. IMT’s holistic approach ensures comprehensive care, addressing both the physical and functional aspects of these conditions to promote long-term recovery and improved quality of life.
Education and Certification
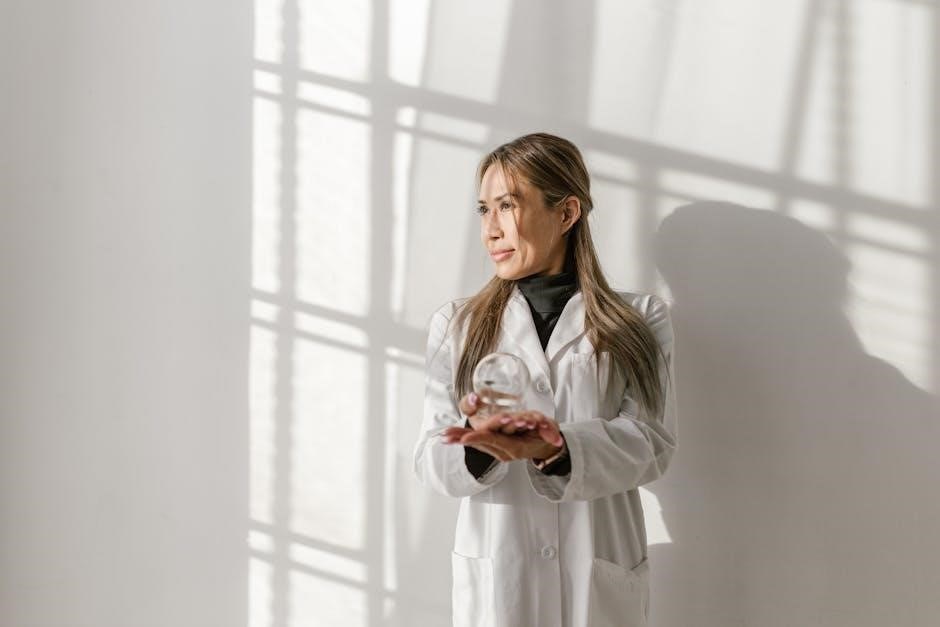

Integrated Manual Therapy certification is an evidence-based, systematic program focusing on advanced manual techniques, exercise integration, and clinical outcomes, ensuring therapists deliver patient-centered, effective care.
4.1 Training Requirements
Becoming an Integrated Manual Therapist requires comprehensive training, starting with a graduate degree in a related field like physical therapy, osteopathy, or chiropractic care. Aspiring therapists must complete hands-on training in manual techniques, including soft tissue mobilization and joint manipulation. Many programs emphasize evidence-based practice, integrating current research into clinical skills. Practitioners typically need hundreds of hours of clinical experience, working under licensed professionals to refine their abilities. Certification programs often require passing rigorous exams to ensure competency in patient assessment, treatment planning, and outcomes-driven care; Continuous education is also essential to stay updated on advancements in the field.
4.2 Certification Programs
Certification in Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) ensures therapists meet standardized competencies. Programs are designed to validate skills in manual techniques, patient assessment, and outcomes-driven care. Many certifications require completion of specialized training, clinical experience, and passing rigorous exams. They emphasize evidence-based practices, ensuring therapists are well-versed in the latest research and techniques. Certification also signals a commitment to patient-centered care and professional development. Advanced certifications may focus on specific areas, such as sports or neurological rehabilitation. These programs help therapists stand out in their field, demonstrating expertise and a dedication to delivering high-quality, integrated care.
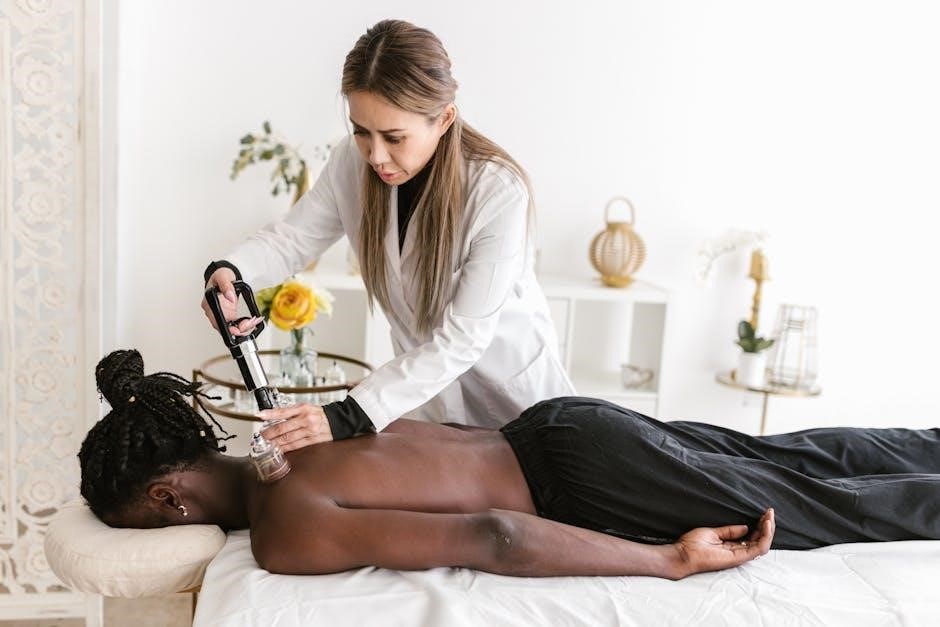

Scientific Evidence and Research
Research supports the efficacy of Integrated Manual Therapy in improving chronic pain and functional outcomes, with studies demonstrating its benefits for various conditions and injuries.
5.1 Efficacy of Integrated Manual Therapy
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) has garnered significant scientific support for its efficacy in addressing various musculoskeletal and neurological conditions. Studies, such as those by G. Bronfort (2010) and B. Bray, highlight its effectiveness in reducing chronic pain, improving joint mobility, and enhancing functional outcomes. IMT’s holistic approach, combining manual techniques with therapeutic exercises, has been shown to promote long-term recovery and prevent recurrences. Its evidence-based framework ensures personalized treatment plans, addressing the root causes of dysfunction. This method is particularly beneficial for conditions like low back pain, where manual therapy, alongside targeted exercises, has proven to be highly effective. The integration of scientific principles with hands-on care underscores IMT’s role as a versatile and reliable therapeutic approach.
5.2 Case Studies and Clinical Outcomes
Case studies demonstrate the positive clinical outcomes of Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) in diverse patient populations. For instance, a study by IC Balán (2016) highlighted improved clinical outcomes when IMT was combined with Motivational Interviewing and BATD. Patients with chronic low back pain experienced a 70% reduction in pain levels after IMT sessions. Another case involving an athlete with a sports injury showed full recovery of joint mobility and strength within six weeks. These outcomes underscore IMT’s effectiveness in addressing both acute and chronic conditions. The therapy’s adaptive nature allows for personalized treatment, leading to enhanced recovery rates and improved quality of life for patients with musculoskeletal and neurological disorders.
The Role of Technology in Modern Practice
Technology enhances integrated manual therapy through AI-driven assessments, telehealth platforms, and digital tools, improving treatment efficiency and patient engagement for better clinical outcomes.
6.1 AI and Digital Tools in Therapy
AI and digital tools are transforming integrated manual therapy by enhancing diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning. AI algorithms analyze patient data to identify patterns and predict outcomes, enabling personalized care. Digital tools, such as wearable devices and mobile apps, monitor progress and engage patients in their recovery; AI-driven platforms also assist therapists in developing tailored exercise programs and tracking adherence; Additionally, virtual reality and augmented reality technologies are being explored to create immersive rehabilitation environments. These innovations not only improve efficiency but also empower patients to take an active role in their therapy, leading to better clinical outcomes and enhanced overall well-being.
6.2 Telehealth and Virtual Consultations
Telehealth and virtual consultations have revolutionized integrated manual therapy by expanding access to care. Patients can now receive remote assessments and guidance, reducing the need for in-person visits. Digital platforms enable therapists to demonstrate exercises, track progress, and provide real-time feedback. Virtual consultations also allow for continuous monitoring of treatment plans, ensuring consistency and adherence. This approach is particularly beneficial for individuals with mobility challenges or those in remote locations. Telehealth tools, such as video conferencing and mobile apps, enhance patient engagement and streamline communication. By leveraging technology, integrated manual therapists can deliver high-quality care more flexibly, improving outcomes and patient satisfaction while reducing costs.